
In harsh environments—automotive door locks, tailgates, charging equipment, smart appliances, outdoor tools—the reliability of a micro switch is often defined by one key requirement: waterproof performance. But what exactly determines whether a micro switch is genuinely waterproof? And how do IP ratings translate into real-world protection?
This article explains the fundamentals behind waterproof micro switches, the meaning of IP (Ingress Protection) ratings, and critical engineering considerations that determine long-term durability.
A waterproof micro switch is engineered to prevent moisture, dust, or other contaminants from entering the internal contact mechanism. Since micro switches rely on precise snap-action structures, even tiny particles or condensation could lead to:
Contact failure
Increased resistance
Shortened lifespan
Safety hazards in automotive or industrial systems
True waterproofing requires a holistic sealing strategy, not just an outer rubber cap.
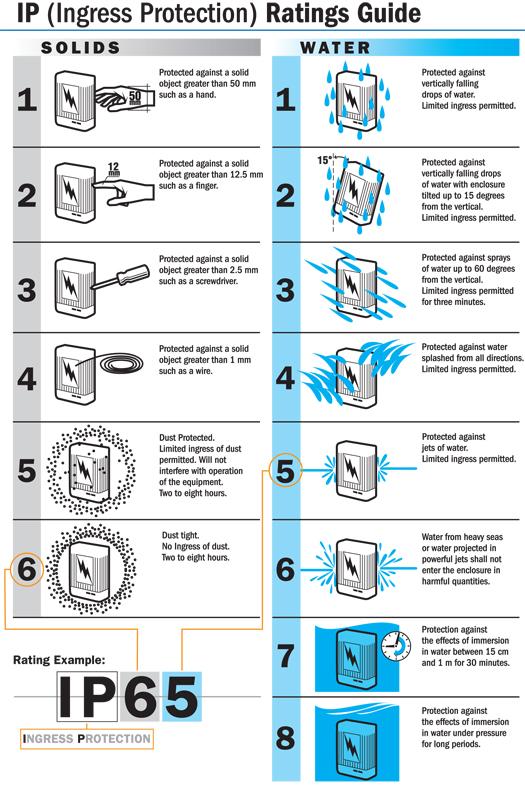
The IP (Ingress Protection) rating is the global standard for defining dust- and water-resistance. It contains two digits:
First digit (0–6): Protection against solid particles
Second digit (0–9K): Protection against water
| IP Level | Meaning | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| IP40 | Protected against objects >1 mm; not water-resistant | Indoor appliances, dashboards |
| IP67 | Fully dust-tight + water immersion up to 1m | Automotive locks, outdoor controls |
| IP68 | Dust-tight + extended immersion | Harsh industrial environments |
| IP6K9K | High-pressure, high-temperature jet spray | Commercial vehicles, heavy machinery |
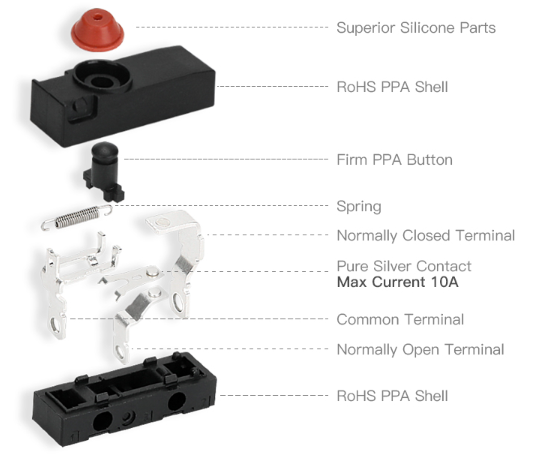
The housing must use high-precision molding with ultra-tight seams. A silicone or fluororubber gasket provides the primary seal.
Terminals are a critical water ingress point. Sealed epoxy resin or molded cavities prevent capillary water flow along lead wires.
A rubber boot, plunger seal, or diaphragm ensures that water cannot enter where the actuator moves.
Even with perfect sealing, the internal structure must withstand humidity and condensation.
High-reliability waterproof micro switches use:
Silver or gold-plated contacts
Corrosion-resistant springs
Anti-arc structures for long life
A reliable waterproof micro switch undergoes rigorous IP testing such as:
Immersion test (IP67/68)
High-pressure spray test (IP6K9K)
Thermal cycling
Humidity exposure
Dust chamber testing
These tests simulate real-world conditions found in automotive door locks, outdoor charging equipment, industrial control panels, and consumer appliances, forming part of the standard validation process used by a qualified micro switch manufacturer to ensure consistent waterproof performance in long-term use.
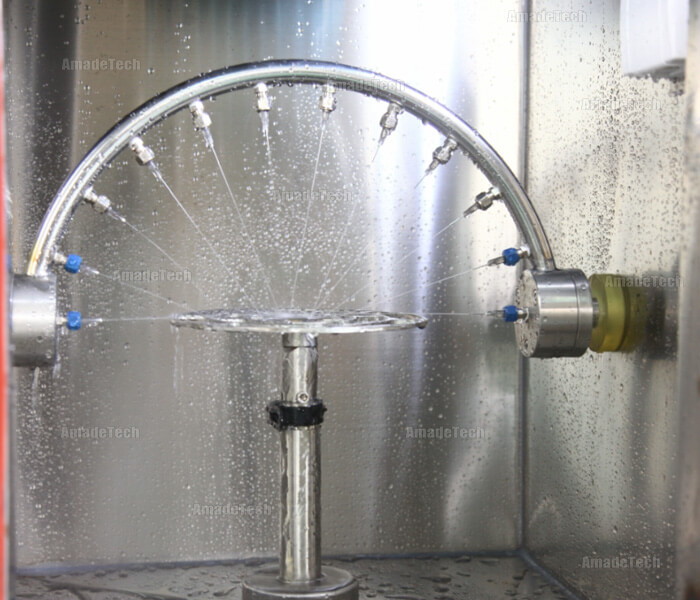

In environments like automotive tailgates, new-energy charging equipment, or outdoor power tools, moisture is inevitable. A waterproof micro switch ensures:
Consistent electrical performance
Long service life
Safety compliance
Reduced maintenance costs
Reliable sensing and control under rain, condensation, or humidity
A micro switch is not truly “waterproof” unless it passes strict IP tests and incorporates professional sealing engineering. Understanding IP ratings—and how they translate into real-world protection—helps engineers select the right component to ensure long-term reliability.
If you need assistance selecting or customizing a waterproof micro switch for automotive, energy, or industrial applications, feel free to ask—I can help you craft specifications or technical documentation.
 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  português
português  tiếng việt
tiếng việt  Türkçe
Türkçe  slovenský
slovenský  slovenčina
slovenčina  беларускі
беларускі 


