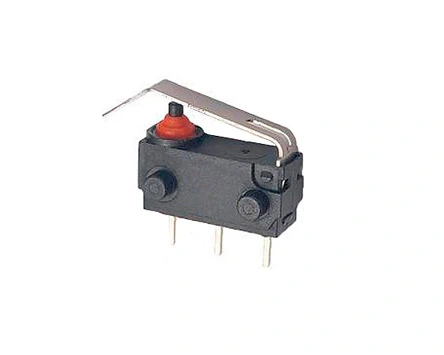
In the vast world of electronic components, the micro switch mini holds an essential place due to its unique functionality and compact design. To truly understand this component, one must focus on its core internal structure — a system both intricate and crucial to its performance.

| Type of Driving Mechanism | Operation Principle | Common Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Button Type | When pressed, the force is transferred via levers and springs to move the contacts. | Common in push-button controls of electronic devices |
| Lever Type | Uses a small external force to generate a larger contact displacement through mechanical leverage. | Ideal for applications requiring high sensitivity and low effort |
| Roller Type | Uses a rotating wheel to adjust contact position, allowing for gradual or repeated switching. | Suitable for circuits needing continuous or adjustable control |



Thanks to their precisely coordinated internal structure, micro switch mini components are extensively used in demanding electronic systems. They play a crucial role in automotive applications, ensuring reliable control in gear detection, door locks, and safety systems. Beyond vehicles, they are also widely adopted in household appliances, new energy charging equipment, power tools, industrial control systems, and gaming devices such as keyboards and mice—functioning as the “nerve endings” that bring responsiveness and reliability to modern electronics.
A deep understanding of the micro switch mini's core structure not only enhances its performance and longevity but also supports more intelligent and durable system design. As technology evolves, these compact yet powerful components will continue to adapt—driving innovation in automotive electronics and enabling smarter control across a wide range of advanced applications.
 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  português
português  tiếng việt
tiếng việt  Türkçe
Türkçe  slovenský
slovenský  slovenčina
slovenčina  беларускі
беларускі